
Data collected by Britain’s Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies, Japanese researchers, and the US Department of Agriculture paint a picture of a growing challenge.

Data collected by Britain’s Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies, Japanese researchers, and the US Department of Agriculture paint a picture of a growing challenge.

The WHO wants a moratorium on COVID-19 booster shots until poorer countries can catch up to richer countries in getting first and second doses of COVID-19 vaccines into the arms of citizens.

The Delta variant is burning through areas in the country where many people are unvaccinated and seems to be targeting younger Americans aged 50 and under and, says one ER physician, they’re “more intensive to care for.”

Should older people get boosters? The data from Israel indicate that this needs to be given strong consideration in those above 60 years old who were fully vaccinated by the end of January.
The CDC data seem to show just how vulnerable even vaccinated people are to the Delta variant.

Investigators in Chile conclude that the lambda COVID-19 variant is not only more infectious than standard SARS-CoV-2, but could also possibly shrug off vaccines. The first case in the United States has been spotted at Houston Methodist Hospital.

The issue of breakthrough infections is increasingly coming up. How frequent are they? How infectious are they? Simply put, we know the COVID-19 vaccines do not offer sterilizing immunity.

Take 5 minutes to catch up on Infection Control Today’s highlights for the week ending July 30.

When the CDC updated masking recommendations earlier this week, the agency also updated COVID-19 testing recommendations.
Israeli announced today that it will begin offering a booster shot to its older citizens to try to stop the spread of the Delta variant. It is the first country in the world to make this move.

In making the announcement, the VA noted that 4 of its employees have died in recent weeks, all of whom were unvaccinated. And 3 died as a direct result of the Delta variant.

New CDC guidelines say that vaccinated individuals should begin wearing masks again when indoors in public settings in parts of the US with substantial to high transmission.
Kevin Kavanagh, MD: “I am convinced this virus is about one or two iterations away from completely avoiding the vaccine. And remember, we have the lambda variant and the kappa variant which are sitting out there in the wings, waiting for immunity to drop and possibly cause another wave.”
Shingrix was originally approved by the FDA in 2017 for the prevention of shingles in adults 50 years and older. Now, it’s approved for those 18 years and older who are immunocompromised.
Not nearly enough Americans are vaccinated to prevent COVID-19 from doing further damage. For some providers, dealing with patients who refuse to do what’s best for them can trigger compassion fatigue.

Take 5 minutes to catch up on Infection Control Today’s highlights for the week ending July 23.
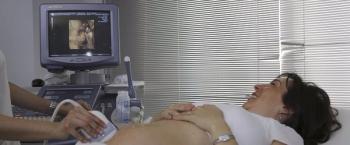
The high-level disinfection process of an ultrasound probe, when indicated, includes documentation that demonstrates high-level disinfection was performed, and patient identifiers were documented to link the ultrasound probe to the patient. This is often referred to as traceability.

For the first time, according to the CDC, health care institutions in the United States have to grapple with a form of C. auris that’s resistant to all antibiotic and antifungal treatments.

Non-ventilator-hospital associated pneumonia prevention is quickly becoming the hot topic among infection preventionists.
Infection preventionists are integral members of the extended sterile processing department team and can be among the department’s biggest supporters.

As the Delta variant is estimated to be around 50% more transmissible than the original strain, the CDC has been emphasizing the need to improve stagnated vaccine rates.

Despite the fact that the processes and layout of the laundry facility met industry standards, infection prevention teams found a significant number of mucormycosis-causing cultures.
The pandemic could leave in its wake a “tsunami” of chronic health conditions in younger people, including serious heart problems.
We need to have a paradigm shift in the way we view this virus, planning and implementing strategies to allow us to live with an endemic pathogen.

Ashish Mathur, PhD: “Today, there are no uniform industry standards to evaluate the efficacy of UVC devices. The onus is up to the infection preventionist to make sure and confirm that whatever claims have been made for the device are being substantiated by clinical evidence and third-party testing.”
Female health care workers under 30 years old are the most likely group to hesitate about getting the COVID-19 vaccine, a study concludes.

Take 5 minutes to catch up on Infection Control Today®’s highlights for the week ending July 16.


New COVID-19 cases in the country are at least 10% higher this week than they were last week. They’ve risen in 46 states, and in 31 states, new cases of SARS-CoV-2 are at least 50% higher.
Seven leading organizations representing health care professionals who routinely battle infections issued a joint statement today saying that COVID-19 vaccinations for health care workers should be mandatory.